stem( Y ) plots the data sequence, Y , as stems that extend from a baseline along the x -axis. The data values are indicated by circles terminating each stem.
stem( X , Y ) plots the data sequence, Y , at values specified by X . The X and Y inputs must be vectors or matrices of the same size. Additionally, X can be a row or column vector and Y must be a matrix with length(X) rows.
stem( ___ , "filled" ) fills the circles. Use this option with any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
stem( ___ , LineSpec ) specifies the line style, marker symbol, and color.
stem( tbl , yvar ) plots the specified variable from the table against the row indices of the table. If the table is a timetable, the specified variable is plotted against the row times of the timetable. To plot one set of y-values, specify one variable for yvar . To plot multiple sets of y-values, specify multiple variables for yvar . (since R2022b)
stem( tbl , xvar , yvar ) plots the variables xvar and yvar from the table tbl . You can specify one or multiple variables for xvar and yvar . If both arguments specify multiple variables, they must specify the same number of variables. (since R2022b)
stem( ___ , Name,Value ) modifies the stem chart using one or more Name,Value pair arguments.
stem( ax , ___ ) plots into the axes specified by ax instead of into the current axes ( gca ). The option, ax , can precede any of the input argument combinations in the previous syntaxes.
h = stem( ___ ) returns a vector of Stem objects in h . Use h to modify the stem chart after it is created.
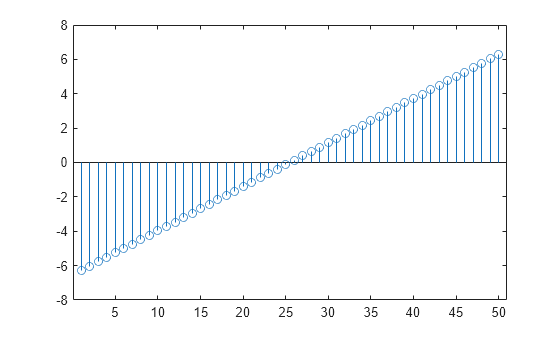
Create a stem plot of 50 data values between - 2 π and 2 π .
figure Y = linspace(-2*pi,2*pi,50); stem(Y)

Data values are plotted as stems extending from the baseline and terminating at the data value. The length of Y automatically determines the position of each stem on the x -axis.
Plot two data series using a two-column matrix.
figure X = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; Y = [cos(X), 0.5*sin(X)]; stem(Y)

Each column of Y is plotted as a separate series, and entries in the same row of Y are plotted against the same x value. The number of rows in Y automatically generates the position of each stem on the x -axis.
Plot 50 data values of cosine evaluated between 0 and 2 π and specify the set of x values for the stem plot.
figure X = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; Y = cos(X); stem(X,Y)
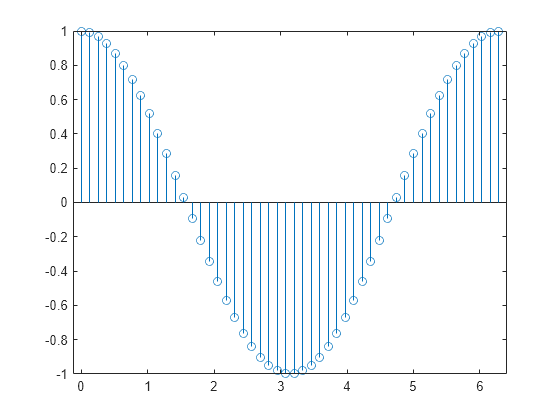
The first vector input determines the position of each stem on the x -axis.
Plot 50 data values of sine and cosine evaluated between 0 and 2 π and specify the set of x values for the stem plot.
figure X = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; Y = [cos(X), 0.5*sin(X)]; stem(X,Y)
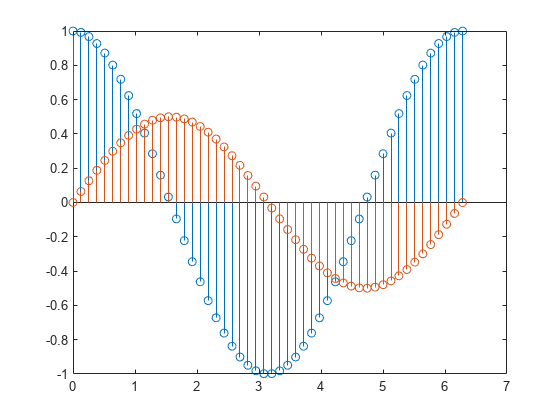
The vector input determines the x -axis positions for both data series.
Plot 50 data values of sine and cosine evaluated at different sets of x values. Specify the corresponding sets of x values for each series.
figure x1 = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; x2 = linspace(pi,3*pi,50)'; X = [x1, x2]; Y = [cos(x1), 0.5*sin(x2)]; stem(X,Y)
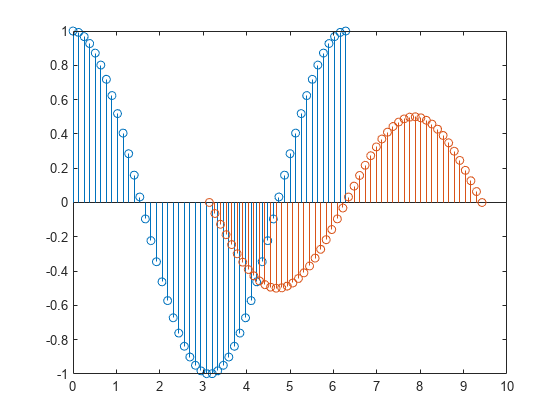
Each column of X is plotted against the corresponding column of Y .
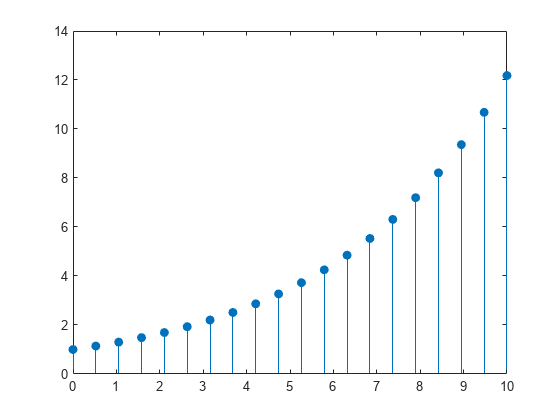
Create a stem plot and fill in the circles that terminate each stem.
X = linspace(0,10,20)'; Y = (exp(0.25*X)); stem(X,Y,'filled')
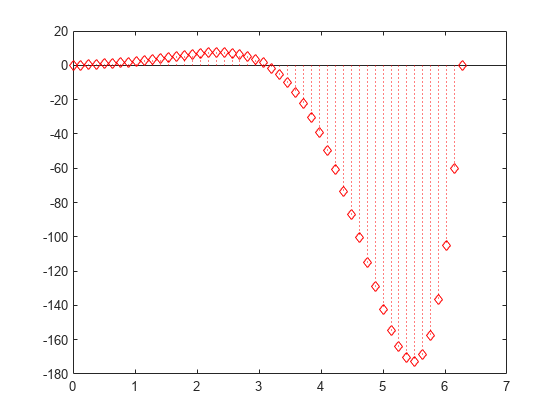
Create a stem plot and set the line style to a dotted line, the marker symbols to diamonds, and the color to red using the LineSpec option.
figure X = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; Y = (exp(X).*sin(X)); stem(X,Y,':diamondr')
To color the inside of the diamonds, use the 'fill' option.
Create a stem plot and set the line style to a dot-dashed line, the marker face color to red, and the marker edge color to green using Name,Value pair arguments.
figure X = linspace(0,2*pi,25)'; Y = (cos(2*X)); stem(X,Y,'LineStyle','-.',. 'MarkerFaceColor','red',. 'MarkerEdgeColor','green')
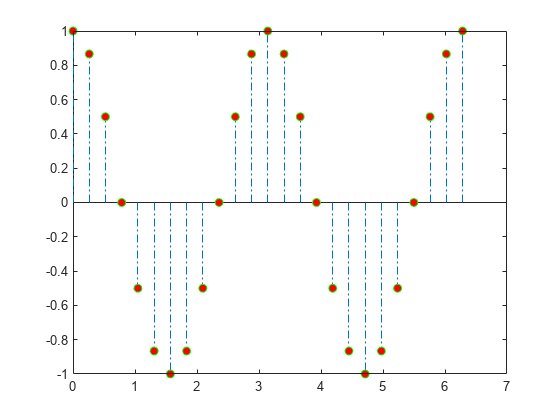
The stem remains the default color.
A convenient way to plot data from a table is to pass the table to the stem function and specify the variables to plot.
Read the first 100 rows and 7 columns of weather.csv as a timetable tbl . Then display the first three rows of the table.
tbl = readtimetable("weather.csv","Range",[1 1 101 7]); head(tbl,3)
Time WindDirection WindSpeed Humidity Temperature RainInchesPerMinute CumulativeRainfall ____________________ _____________ _________ ________ ___________ ___________________ __________________ 25-Oct-2021 00:00:09 46 1 84 49.2 0 0 25-Oct-2021 00:01:09 45 1.6 84 49.2 0 0 25-Oct-2021 00:02:09 36 2.2 84 49.2 0 0
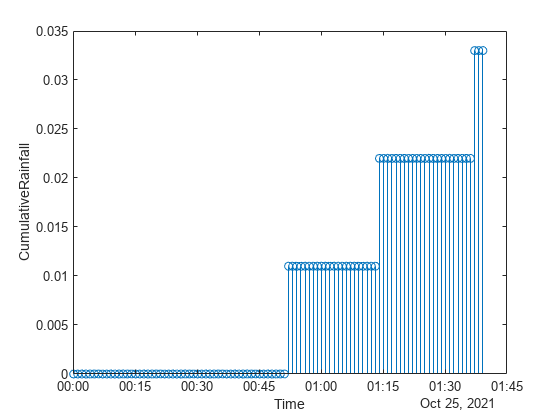
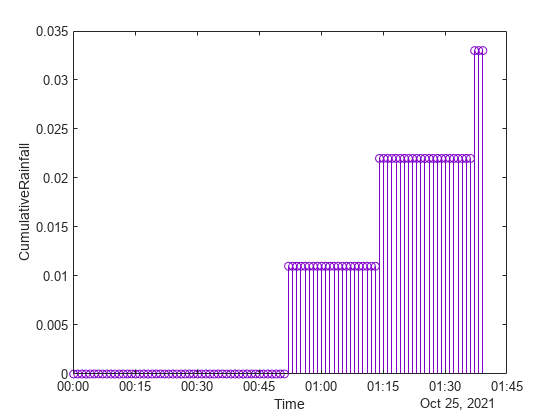
Plot the row times on the x -axis and the CumulativeRainfall variable on the y -axis. When you plot data from a timetable, the row times are plotted on the x -axis by default. Thus, you do not need to specify the Time variable. Return the Stem object as h . Notice that the axis labels match the variable names.
h = stem(tbl,"CumulativeRainfall");
Change the color of the plot to purple by setting the Color property.
h.Color = [0.5 0 0.8];
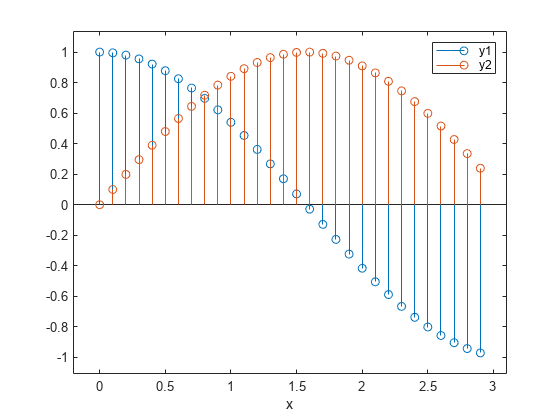
Create vectors x , y1 , and y2 , and use them to create a table. Plot the y1 and y2 variables against the x variable, and use the axis padded command so that the stems do not overlap with the plot box. Then add a legend, and notice that the legend labels match the table variable names.
x = (0:0.1:2.9)'; y1 = cos(x); y2 = sin(x); tbl = table(x,y1,y2); stem(tbl,"x",["y1","y2"]); % Pad axes and add a legend axis padded legend
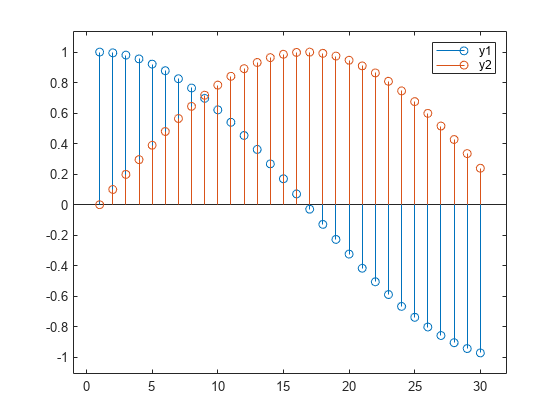
Alternatively, you can omit the x variable and plot the y1 and y2 variables against the row indices of the table.
stem(tbl,["y1","y2"]); axis padded legend
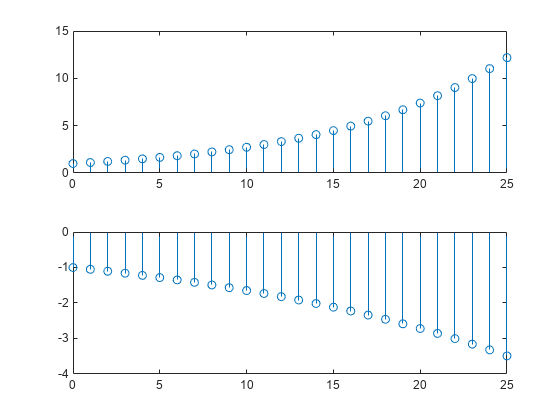
You can display a tiling of plots using the tiledlayout and nexttile functions. Call the tiledlayout function to create a 2-by-1 tiled chart layout. Call the nexttile function to create the axes objects ax1 and ax2 . Create separate stem plots in the axes by specifying the axes object as the first argument to stem .
x = 0:25; y1 = exp(0.1*x); y2 = -exp(.05*x); tiledlayout(2,1) % Top plot ax1 = nexttile; stem(ax1,x,y1) % Bottom plot ax2 = nexttile; stem(ax2,x,y2)
Create a 3-D stem plot and return the stem series object.
X = linspace(0,2); Y = X.^3; Z = exp(X).*cos(Y); h = stem3(X,Y,Z,'filled');
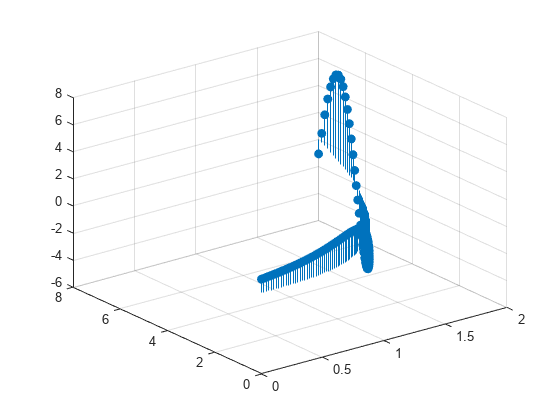
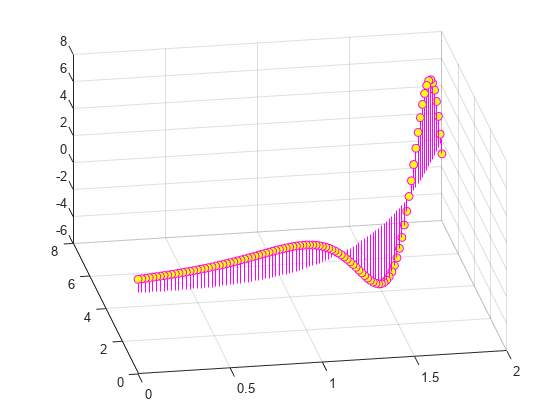
Change the color to magenta and set the marker face color to yellow. Use view to adjust the angle of the axes in the figure. Use dot notation to set properties.
h.Color = 'm'; h.MarkerFaceColor = 'y'; view(-10,35)
Create a stem plot and change properties of the baseline.
X = linspace(0,2*pi,50); Y = exp(0.3*X).*sin(3*X); h = stem(X,Y);
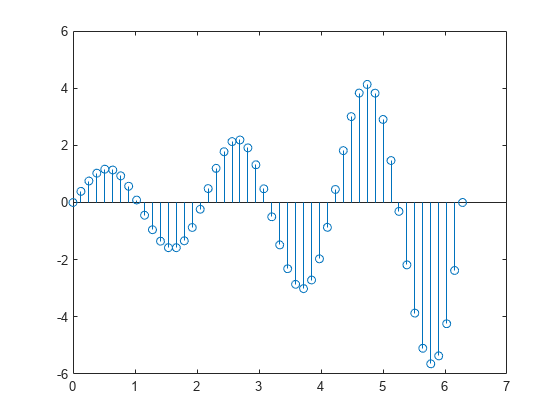
Change the line style of the baseline. Use dot notation to set properties.
hbase = h.BaseLine; hbase.LineStyle = '--';
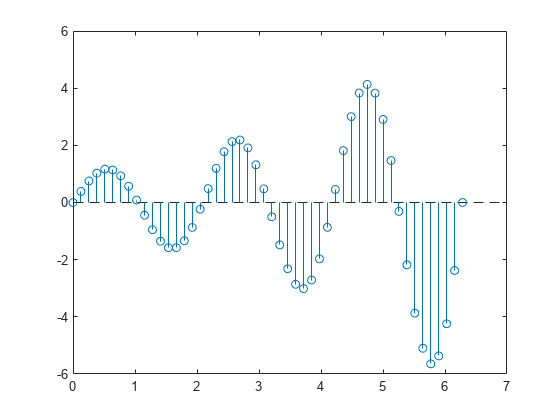
Hide the baseline by setting its Visible property to 'off' .
hbase.Visible = 'off';
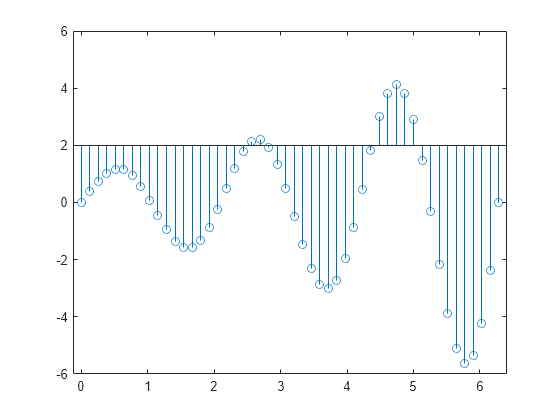
Create a stem plot with a baseline level at 2.
X = linspace(0,2*pi,50)'; Y = (exp(0.3*X).*sin(3*X)); stem(X,Y,'BaseValue',2);
Data sequence to display, specified as a vector or matrix. When Y is a vector, stem creates one Stem object. When Y is a matrix, stem creates a separate Stem object for each column.
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | categorical | datetime | duration
Locations to plot data values in Y , specified as a vector or matrix. When Y is a vector, X must be a vector of the same size. When Y is a matrix, X must be a matrix of the same size, or a vector whose length equals the number of rows in Y .
Data Types: single | double | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | categorical | datetime | duration
Line style, marker, and color, specified as a string scalar or character vector containing symbols. The symbols can appear in any order. You do not need to specify all three characteristics (line style, marker, and color). For example, if you omit the line style and specify the marker, then the plot shows only the marker and no line.
Example: "--or" is a red dashed line with circle markers.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Source table containing the data to plot, specified as a table or a timetable.
Table variables containing the y-coordinates, specified using one of the indexing schemes from the table.
The table variables you specify can contain numeric, categorical, datetime, or duration values. If xvar and yvar both specify multiple variables, the number of variables must be the same.
Example: stem(tbl,"x",["y1","y2"]) specifies the table variables named y1 and y2 for the y-coordinates.
Example: stem(tbl,"x",2) specifies the second variable for the y-coordinates.
Example: stem(tbl,"x",vartype("numeric")) specifies all numeric variables for the y-coordinates.
Table variables containing the x-coordinates, specified using one of the indexing schemes from the table.
The table variables you specify can contain numeric, categorical, datetime, or duration values. If xvar and yvar both specify multiple variables, the number of variables must be the same.
Example: stem(tbl,["x1","x2"],"y") specifies the table variables named x1 and x2 for the x-coordinates.
Example: stem(tbl,2,"y") specifies the second variable for the x-coordinates.
Example: stem(tbl,vartype("numeric"),"y") specifies all numeric variables for the x-coordinates.
Axes object. If you do not specify the axes, then stem plots into the current axes.
Specify optional pairs of arguments as Name1=Value1. NameN=ValueN , where Name is the argument name and Value is the corresponding value. Name-value arguments must appear after other arguments, but the order of the pairs does not matter.
Before R2021a, use commas to separate each name and value, and enclose Name in quotes.
Example: "LineStyle",":","MarkerFaceColor","red" plots the stem as a dotted line and colors the marker face red.
The Stem properties listed here are only a subset. For a complete list, see Stem Properties .
Line style, specified as one of the options listed in this table.
Line width, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch. If the line has markers, then the line width also affects the marker edges.
The line width cannot be thinner than the width of a pixel. If you set the line width to a value that is less than the width of a pixel on your system, the line displays as one pixel wide.
Stem color, specified as an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB ® uses in many types of plots.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Example: "blue"
Example: [0 0 1]
Example: "#0000FF"
Marker symbol, specified as one of the markers listed in this table.
Example: "+"
Example: "diamond"
Marker size, specified as a positive value in points, where 1 point = 1/72 of an inch.
Marker outline color, specified as "auto" , an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. The default value of "auto" uses the same color as the Color property.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Here are the RGB triplets and hexadecimal color codes for the default colors MATLAB uses in many types of plots.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Marker fill color, specified as "auto" , an RGB triplet, a hexadecimal color code, a color name, or a short name. The "auto" option uses the same color as the Color property of the parent axes. If you specify "auto" and the axes plot box is invisible, the marker fill color is the color of the figure.
For a custom color, specify an RGB triplet or a hexadecimal color code.
Alternatively, you can specify some common colors by name. This table lists the named color options, the equivalent RGB triplets, and hexadecimal color codes.